In a world where technical knowledge is as valuable as raw materials, licensing know-how emerges as a crucial bridge between expert knowledge and business opportunities. This practice, which involves the transfer of specialized technical skills and unique methodologies, opens fascinating avenues for the monetization of knowledge.
This article delves into the heart of licensing know-how, revealing how it shapes the landscape of modern innovation and transforms expertise into financial success.
The Concept of Licensing Know-How
In the business arena, licensing know-how stands as a strategic tool, offering a distinct competitive advantage. It not only allows for the preservation of unique knowledge but also paves the way for fruitful collaborations.

Definition and Importance
licensing know-how is an agreement where the holder (the licensor) grants another party (the licensee) the right to exploit their specific know-how, such as a unique manufacturing process.
This transmission of knowledge and skills, which can include non-patented commercial and/or industrial information, is done in exchange for compensation, often a lump sum or proportional fee.
Unlike industrial property rights, know-how does not confer an exploitation monopoly, but its value lies in its transmissible, substantial, and secretive nature.
Advantages and Applications
Know-how, encompassing a set of technical, practical knowledge and tips often accumulated over years of experience, is crucial in areas where solutions are not always formalized but result from practical expertise.
It can be likened to deep learning in artificial intelligence, where effective problem-solving is achieved through an intuitive understanding gained over time. In a licensing contract, it is essential to precisely list the elements of the know-how being transferred.
Although know-how is not protected like patented industrial property, it can be financially valued and represent a significant intangible asset for a company.

Strategies for Knowledge Transfer
Effective transfer of know-how is a central pillar in the implementation of knowledge licenses. This requires well-designed methods and suitable teaching techniques to ensure that knowledge is not only transmitted but also fully assimilated by the licensee.
Techniques for Knowledge Transfer
The transfer of know-how is a delicate process that requires a methodical and thoughtful approach. Here’s a more detailed development of key techniques:
Practical Workshops
Practical workshops are essential for complete immersion in the know-how. In these sessions, licensees can directly experience techniques under the supervision of experts. These workshops provide the opportunity to put theoretical knowledge into practice in a real context, allowing participants to understand the nuances and practical applications of know-how. Furthermore, these workshops encourage questions and discussions, thus creating a dynamic and interactive learning environment.
Visual Aids and Demonstrations
The use of visual aids such as videos, graphics, and infographics makes learning more accessible and engaging. These tools help to visualize complex concepts and demonstrate step-by-step procedures, which is particularly useful in technical fields. In addition, practical demonstrations by experts offer a live insight into processes in action, allowing licensees to see best practices in operation.
Interactive Exercises
Interactive exercises are designed to reinforce learning and encourage the practical application of knowledge. Through simulations and role-playing, licensees can test their understanding and refine their skills. These activities also promote the development of problem-solving and critical thinking, essential skills for applying know-how in real situations.
Supplementary Documentation
Providing procedure manuals, operation guides, and supplementary documentation is crucial for ongoing learning. These resources serve as reliable references and can be consulted long after the initial training is over, helping licensees to refresh and deepen their understanding of the know-how.
Holistic Approach
Adopting a holistic approach means going beyond the simple transmission of technical skills. It involves encouraging a deep understanding of the philosophy and principles underlying the know-how. This comprehensive approach helps licensees to integrate the know-how into their own work context, allowing them to innovate and adapt the acquired skills to their specific needs.
By combining these transmission techniques, licensors can ensure a complete and effective transfer of know-how, thus preparing licensees to use this knowledge independently and innovatively in their own operations.
Practical Cases of Knowledge Transfer
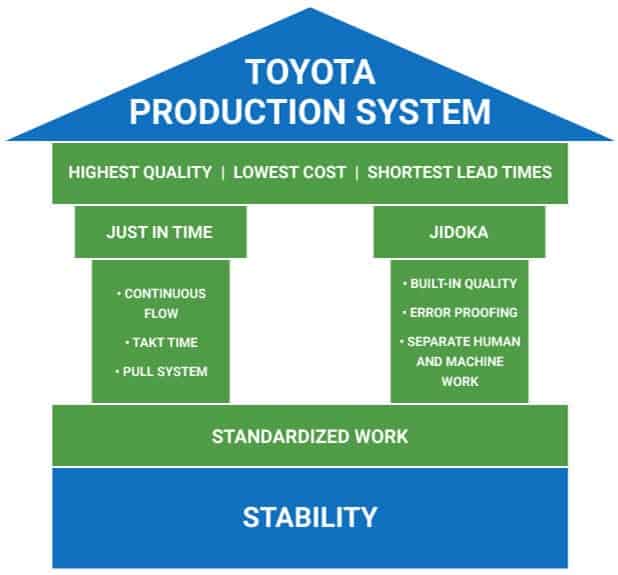
The real value of know-how transfer methods is manifested through concrete and recognized examples. Take, for instance, Toyota in the automotive industry.
The company is famous for its Toyota Production System (TPS), a unique know-how in production management and operational efficiency.
Toyota has shared this know-how with its suppliers and even other automobile manufacturers through training programs and partnerships, significantly improving quality and efficiency across the industry.
In the field of haute cuisine, the case of the Ducasse group is a striking example. Alain Ducasse, a renowned chef, has expanded his culinary empire by training other chefs and food service professionals in his exclusive culinary methods and techniques.
Ducasse-licensed establishments maintain a high level of quality and excellence, reflecting Ducasse’s know-how and expertise, thanks to a rigorous and structured transmission of his culinary knowledge.


These examples illustrate the significant impact of know-how transfer in various sectors. It not only allows for the preservation and transmission of valuable technical skills but also ensures the quality and authenticity of products and services offered under the brand or name of the original company.
Monetizing Expertise
Turning expertise into a tangible source of revenue is a major challenge for companies possessing specialized knowledge and skills. This section explores the various ways businesses can monetize their expertise, effectively converting expertise into profits.
Monetization Models
Monetizing expertise can take several forms, each suited to different types of knowledge and markets. Here are some common models:
Licenses and Royalties : The most direct method is to grant licenses for the use of expertise to other companies, in exchange for royalties. This allows the licensor to generate regular income while retaining ownership of their expertise.
Training and Consulting : Offering training and consulting services is another way to monetize expertise. Businesses and experts can provide specialized training or offer strategic advice, charged at a predefined rate.
Partnerships and Joint Ventures : Engaging in partnerships or creating joint ventures allows for monetizing expertise by collaborating on new products or services. This enables sharing risks while leveraging each partner’s skills.
Selling Derived Products or Services : Developing products or services that embody the expertise and selling them directly in the market. This could include software, tools, or even educational kits.

Pricing Strategies
Determining a pricing strategy for expertise is a delicate task that requires a deep understanding of its intrinsic value and its impact on the market. The first step in this approach is the analysis of the value of the expertise. This involves assessing its rarity, market demand, and the specific benefits it provides to licensees. This analysis allows setting a price that reflects not only the value of the expertise but also its relevance and usefulness to the customer.
A flexible approach to pricing is often advantageous. Businesses can adapt their prices based on various factors, such as the type of client, industry sector, and the specific nature of the expertise. For example, a performance-based pricing structure or variable pricing according to circumstances can be more appealing and relevant for certain types of licensees. This flexibility allows businesses to stay competitive and aligned with changing market trends and conditions.
Considering long-term contracts can also be a wise strategy, as it ensures a stable and predictable source of income. These contracts can include price adjustment clauses to account for market fluctuations or changes in the value of the expertise over time. This enables businesses to maintain fair and balanced pricing, even in a dynamic business environment.
Finally, regular evaluation and reevaluation of the expertise are crucial. The market evolves, as does the nature and impact of the expertise. By periodically reassessing their expertise, businesses can adjust their pricing to ensure it remains in line with its current and future impact on the market. This dynamic approach to pricing ensures that the expertise is not only properly valued but also remains a viable and attractive commercial asset in the long term.
Practical Cases and Success Stories
Licensing know-how licensing has proven to be a decisive success factor for numerous international companies. From Coca-Cola to Intel, there are abundant examples demonstrating how effective management of know-how can pave the way for remarkable commercial successes and significant expansion across various sectors.
Success in Various Industries

By licensing to regional bottlers, Coca-Cola has managed to expand its global reach while preserving the consistency and uniqueness of its product.
Intel, on the other hand, has capitalized on its innovations in the semiconductor field. By licensing its processor technologies, Intel has not only consolidated its market leadership position but also established industrial standards, thus influencing the entire semiconductor industry.

Challenges and Solutions
In the process of licensing know-how , companies face several challenges, particularly in terms of risk management and knowledge protection. Identifying and effectively resolving these challenges is crucial to ensure that know-how remains a valuable and protected asset.
Risk Management
Risk management in licensing know-how involves taking precautions to protect the interests of the business. It’s crucial to conduct detailed risk assessments before entering into a licensing agreement. These assessments should consider potential risks of unauthorized disclosure, misuse of the know-how, or non-compliance with contract terms.
To mitigate these risks, it’s recommended to implement solid confidentiality agreements and specific contractual clauses that clearly define terms of use, restrictions, and consequences in case of violation. It’s also important to choose reliable and reputable licensing partners, capable of respecting and valuing the shared know-how.
Protection and Security of Knowledge

Protecting and securing the know-how in the context of licensing is another major challenge. This starts with clear and detailed documentation of the know-how, including procedures, techniques, and specific knowledge. This documentation serves as a reference for the licensee and helps to prevent misunderstandings or incorrect interpretations.
Furthermore, implementing security measures to protect the know-how is essential. This can include secure information management systems, restricted access protocols, and training employees on aspects of confidentiality and security.
Establishing mechanisms for regular monitoring and control ensures that the know-how is used in accordance with the terms of the license and that its value is preserved. In case of a breach, it is important to have clear procedures to intervene quickly and effectively.
By proactively addressing these challenges and implementing adequate strategies for risk management and knowledge protection, companies can maximize the benefits of licensing know-how while minimizing potential risks. This ensures that the know-how remains a sustainable competitive advantage and a valuable business asset.
Conclusion: The Future of Licensing Know-How
As we have seen throughout this article, licensing know-how is more than just a commercial transaction. It represents a synergy between the transmission of unique knowledge and the creation of economic value. Companies that master the art of licensing know-how , like Coca-Cola with its secret formula or Intel with its semiconductor technologies, have shown how this model can be a source of growth and innovation.
Looking to the future, licensing know-how is likely to play an even more crucial role in a world where innovation and specialization are becoming essential for competitiveness. With the rapid evolution of technologies and the rise of the knowledge economy, the ability to effectively share specialized knowledge while protecting and monetizing it becomes a major strategic asset.
Challenges, particularly in terms of risk management and knowledge protection, will remain central concerns. Companies will need to continue innovating in their approaches to licensing know-how, adapting their strategies to the changing needs of the market and new technological realities.
In conclusion, licensing know-how is not just a business strategy, but also a driver of innovation and knowledge sharing. By continuing to evolve and adapt, it offers exciting prospects for companies looking to fully exploit their intellectual potential and influence the future of their industry.
Monte-Carlo Lifestyle is a brand that encapsulates all the collections in its portfolio, with the labels ‘Monaco’ and ‘Monte-Carlo, that is registered globally for an extensive line of consumer goods.
Subscribe for our monthly newsletter to stay updated.
which supplier and need to make the complete setup, can be added later ?

















