In a world where brand image is synonymous with power and market presence, understanding and navigating the world of brand licensing has become a strategic imperative for companies wishing to extend their influence and protect their identity.
Brand licensing offers a unique opportunity for growth and international collaboration, enabling companies to expand beyond their traditional borders while retaining control of their image and values.
This article explores the many facets of brand licensing, highlighting its crucial role in global trade and international distribution strategies.
Brand Licence
Trademark licensing is a powerful tool in the world of international business. It allows a company (the licensor) to grant another entity (the licensee) the right to use its brand to market products or services. This approach offers unprecedented flexibility for companies seeking to expand into new markets, without diluting their brand essence.
Definition and Importance in Global Trade
Brand licensing is more than just a commercial agreement; it is a strategy that enables companies to expand globally. By granting rights to use their brand, companies can exploit new market opportunities, reach wider audiences and generate additional revenue, while maintaining strict control over how their brand is used.
This mechanism is crucial to preserving the integrity and value of the brand in an increasingly competitive and globalised business environment.
Central role in International Distribution Strategies
Brand licences play a central role in the formulation of international distribution strategies. They enable rapid expansion into new territories while minimising the risks and investments usually associated with such growth.
This approach offers companies a flexible way of introducing their products and services to new markets, relying on local partners who have a better understanding of the specific dynamics of the market.
Apple Inc. and Compatible Accessories
An emblematic example of the effective use of brand licensing is that of Apple Inc. By licensing the creation of accessories compatible with its products, Apple has not only
extended the ecosystem of its devices but has also strengthened the quality and user experience associated with its brand.
This strategy allows third parties to develop complementary products, while ensuring that they meet Apple’s high standards.
This is a perfect example of how a company can extend its reach while preserving the consistency and quality of its brand.

Fundamentals of the Trademark Licence Agreement
The nature and scope of a brand licence are essential to establishing a beneficial commercial relationship between licensor and licensee. This contract, which is the cornerstone of many distribution and marketing agreements, must be carefully designed to meet the needs of both parties and to protect their respective interests.
Nature and Scope of a Trademark Licence
A trademark licence contract is an agreement whereby the owner of a trademark (the licensor) grants another party (the licensee) the right to use that trademark within a defined framework. The scope of the licence can vary considerably: it may be limited to certain products or services, to specific geographical regions, and may be exclusive or non-exclusive.
This type of contract enables the licensee to exploit the brand’s reputation for its own benefit, while generating income for the licensor.

Registration Process and Global Implications
For a trademark licence to be effective and legally binding, it is essential that the trademark is properly registered.
Trademark registration offers legal protection and ensures that the licensor has exclusive rights to the use of the trademark. In a global context, this means navigating the different trademark registration systems in various countries, each with its own rules and regulations.
A properly registered and managed trademark provides a solid foundation for a successful and secure licensing agreement.
Adidas and its Licensed Products
Adidas, the German sportswear giant, exemplifies the effectiveness of a well-executed brand licensing strategy with its partnership with Delta Galil.
This collaboration has enabled Adidas to significantly expand its product range by entrusting Delta Galil, a renowned textile specialist, with the production of underwear and sportswear under the Adidas brand.
This strategic agreement combines Delta Galil’s manufacturing expertise with the power of the Adidas brand, ensuring that each product adheres to Adidas’ rigorous standards in terms of quality, comfort, and design.
This synergy between the two companies strengthens Adidas’ global market presence while maintaining the brand’s commitment to excellence and innovation.

Key elements of a Trademark Licence Agreement
Drawing up a brand licensing agreement requires careful attention to a number of key elements. These elements ensure that the contract is not only beneficial to both parties, but also protects their rights and interests.
The ownership of the brand, the definition of the target territories and markets, as well as the duration and financial terms are among the most crucial aspects to consider when drafting a licence agreement.
Trademark Ownership and Transfer of Rights
Trademark ownership is fundamental to any licensing agreement. It designates who owns the rights to the trademark and is entitled to grant a licence for its use. Before entering into a licensing agreement, it is crucial to check that the licensor actually owns the rights to the trademark and is legally authorised to transfer these rights.
This often involves a prior art search to ensure that the trademark is free from any potential conflict with existing trademarks, and that the licensor holds valid legal protection for the trademark.
Definition of target territories and markets
The definition of target territories and markets is another essential element of a brand licensing agreement. This clause specifies the geographical areas where the licensee is authorised to use the brand. It can include entire countries, specific regions or even niche markets.
This definition must be clear and precise to avoid any misunderstanding or potential conflict over the authorised marketing areas.
Duration and financial terms of the licence
The duration of the licence contract and the financial terms constitute the economic framework of the agreement. The duration can vary from a few years to a long-term agreement, depending on the objectives and strategies of both parties.
The financial terms, generally comprising royalties or licence fees, must be clearly defined. These terms include the amount of payments, the frequency, the methods of calculating royalties and the terms of payment.
Example of Brand Strategy: Coca-Cola

A concrete example of Coca-Cola’s brand licensing strategy is exemplified by its longstanding partnership with Swire Beverages. Swire, a major player in food production and distribution since the 1880s, became a strategic partner of Coca-Cola in the mid-1960s. Today, Swire Coca-Cola holds the exclusive rights to manufacture, market, and distribute Coca-Cola products in 11 provinces and the Shanghai Municipality in Mainland China, as well as in the Hong Kong SAR, Taiwan region, Vietnam, Cambodia, and an extensive area of the western USA.
This collaboration is part of Swire’s long tradition in the beverages and food chain sector, dating back to the establishment of the Taikoo Sugar Refinery in Hong Kong. Swire also has historical interests in tea cultivation and trading since 1976, with its stake in James Finlay, one of the world’s oldest tea producers, now a wholly-owned subsidiary of the group. Finlays, under Swire’s wing, is today a leading international supplier of tea, coffee, and natural ingredients for the global beverage industry.
Furthermore, Swire is one of the largest operators of cold storage facilities in the USA, further reinforcing its key role in logistics and distribution in the food and beverage sector.
The partnership between Coca-Cola and Swire Beverages is a model of success in brand licensing, allowing Coca-Cola to benefit from Swire’s local and global expertise in distribution and marketing, while ensuring consistent quality and coherence of Coca-Cola products in international markets.

Brand Licensing vs Franchising: An International Comparison
The distinction between brand licensing and franchising is crucial in the world of international business. Although these two strategies share certain aspects, there are fundamental differences in terms of structure, commitments and responsibilities.
Understanding these differences is essential for companies looking to expand their brand globally.
Key Differences and Strategic Considerations
The main contrast between a brand licence and a franchise lies in the scope of the agreement. A brand licence is generally more limited, focusing on the right to use the brand for specific products or services.
A franchise, on the other hand, includes not only the licence of the brand, but also the transfer of complete commercial know-how, operational processes, and often ongoing assistance from the franchisor.
In a franchise, the franchisor provides a proven business model, training, marketing and operational guidelines, which is generally not the case in a simple brand licence.
Franchisees therefore undertake not only to use the brand, but also to follow a specific set of business practices.
The McDonald's Global Model
McDonald’s is a perfect example of the franchise model. As a franchisor, McDonald’s not only provides its brand to its franchisees, but also a complete business system, including training, equipment, management techniques and service standards. This model enables McDonald’s to guarantee a consistent customer experience in its thousands of restaurants around the world.
McDonald’s franchisees benefit from the brand’s reputation, but must also adhere strictly to the methods and standards established by the franchisor. This level of control and support is much greater than in a simple brand licence, where the licensee generally has more freedom in exploiting the brand.
The distinction between brand licensing and franchising, as illustrated by the McDonald’s model, highlights the importance of a strategy tailored to a company’s specific vision and objectives. While licences offer greater flexibility and freedom in the use of the brand, franchises offer a complete package, including not only the brand, but also a proven business model and ongoing support. This strategic choice largely depends on the company’s ambitions, its desire to expand and its commitment to consistency of customer experience across the world.

Source : Wisevoter
Brand protection and enhancement through licensing
When it comes to brand licensing, the protection and enhancement of a brand’s image are essential. These agreements, when well structured, can not only extend the reach of a brand, but also enhance its prestige and perceived value. A meticulous strategy is required to ensure that the brand is not diluted or misrepresented across the various licence implementations.
Strategies for preserving brand integrity
Preserving the integrity of the brand in a licensing agreement means establishing clear guidelines for the use of the brand. It is crucial to define the standards that the licensed products or services must meet, in order to ensure a faithful representation of the brand.
This includes specifications on quality, design, presentation and even the marketing associated with the brand. In addition, it is important to plan regular checks and audits to ensure that these standards are continually met.

Image Management and Quality Standards
Effective management of the brand’s image and maintenance of quality standards are paramount in a licensing agreement. This often involves the establishment of a graphic
charter and communication guidelines to ensure that the brand image is consistent across all media and regions.
Licensees need to understand the importance of these standards in maintaining the brand’s reputation and identity, ensuring a consistent experience for customers, regardless of their geographical location.
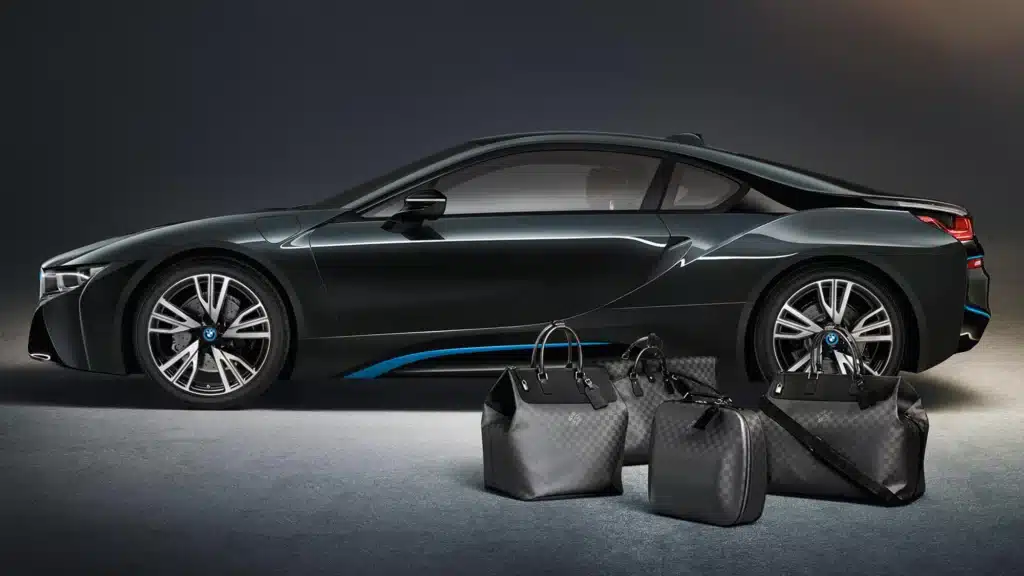
Luxury example: Louis Vuitton's strategy

In its strategy for brand protection and enhancement, Louis Vuitton entered into an exceptional partnership with BMW, exemplifying the perfect harmony between luxury and innovation. This collaboration came to life with the creation of an exclusive line of custom luggage, specifically designed to fit seamlessly into the luxurious interiors of BMW vehicles.
Each item in this exclusive collection, ranging from suitcases to travel bags, was crafted with the attention to detail characteristic of Louis Vuitton, using the highest quality materials and featuring the brand’s iconic monogram. This partnership allowed Louis Vuitton not only to extend its presence into the world of luxury automotive design but also to reinforce its brand image as a symbol of elegance and innovation.
This collaboration between Louis Vuitton and BMW also highlighted the luxury brand’s ability to maintain its high standards in design and quality while adapting to new and diverse contexts. Louis Vuitton’s meticulous strategy in selecting its licensing partners and preserving the integrity of its brand has thus contributed to reinforcing its iconic status in the global luxury sector.

Legal aspects and trademark registration
When it comes to brand licensing, legal aspects and brand registration play a crucial role. These components are fundamental to ensuring the validity and legal protection of licensing agreements and to avoiding potential disputes.
Understanding the legal implications is essential for all companies looking to establish or expand their brand licensing network internationally.
Importance of Registration and Legal Protection
Trademark registration is an essential step in establishing a solid legal basis for any licensing agreement. By registering the trademark, the licensor obtains exclusive rights over its use, enabling it to control and regulate its use by third parties. Registration protects the brand against unauthorised use and counterfeiting, ensuring that the brand owner retains its power and influence in the marketplace. It is a process that varies from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, but is universally recognised as a prerequisite for the effective protection of intellectual property.
Global implications for Brands and Licences
In a global context, brand registration takes on an added dimension due to the diversity of legal systems and registration procedures in different countries.
For a brand wishing to extend its international reach through licensing, understanding and navigating this diverse legislation is crucial.
A well-planned registration strategy ensures that the brand is protected in all the key territories in which it operates or plans to operate, thus avoiding brand conflicts and intellectual property disputes.
Mutual benefits of Brand Licences
The world of brand licensing offers fertile ground for significant mutual benefits for both licensors and licensees. This symbiotic dynamic between the two parties not only enables expansion and diversification for the licensor, but also offers the licensee the opportunity to partner with established and respected brands, opening up new commercial avenues.
Gains for the Licensor and Opportunities for the Licensee
For the licensor, brand licences represent a source of additional revenue without the costs and risks associated with setting up new subsidiaries or expanding directly into new markets. They also extend the brand’s reach and enhance its visibility in different markets and consumer segments.
For the licensee, access to a recognised and respected brand can significantly boost the credibility and appeal of its offerings, making it easier to penetrate the market and attract loyal customers.
Example of Synergy: Collaboration between Disney and its Partners
Disney is a perfect example of the synergy created by brand licensing. By collaborating with various partners on products ranging from toys to clothing, Disney extends its influence while allowing these companies to benefit from the appeal of its iconic characters and stories.
These partnerships are carefully chosen to align with Disney’s image and values, ensuring brand consistency while providing licensees with a valuable platform to develop their businesses.
For example, the collaboration between Disney and LEGO to create themed play sets has not only generated revenue for Disney, but has also enabled LEGO to broaden its product offering and attract new consumer segments.
These strategic alliances between Disney and its partners demonstrate how brand licensing can create win-win opportunities, stimulating innovation and growth for all parties involved.


Conclusion: Exploiting the potential of Brand Licensing
Brand licensing is a powerful and versatile strategy for companies seeking to extend their influence and strengthen their position in the global marketplace. This conclusion aims to summarise the key benefits of brand licensing and offer a forward-looking view of how it can be used strategically to drive growth and innovation.
Summary of Global Benefits and Strategic Advice
Brand licensing offers considerable benefits, particularly in terms of diversifying revenues, expanding brand reach and consolidating brand image. For companies, adopting a strategic approach to establishing and managing brand licences is essential.
It is important to carefully select partners aligned with the brand’s values and image, to clearly define the terms of the contract, and to ensure adequate legal protection for the brand. In addition, maintaining quality control and brand consistency across the various licence implementations is crucial to maximising profits while preserving brand integrity.
Proactive Vision for the Future of Brand Licensing
The future of brand licensing is looking bright, with growing opportunities in an ever-changing global marketplace. Companies that take a proactive view and integrate brand licensing into their overall strategy will be better placed to navigate changing market dynamics and exploit new opportunities.
By staying ahead of consumer trends and being receptive to innovation, companies can use brand licensing not only to expand geographically, but also to enter new market segments and respond creatively to consumer needs.
Monte-Carlo Lifestyle is a brand that encapsulates all the collections in its portfolio, with the labels ‘Monaco’ and ‘Monte-Carlo, that is registered globally for an extensive line of consumer goods.
Subscribe for our monthly newsletter to stay updated.
which supplier and need to make the complete setup, can be added later ?

















